Moringa, also known as the "miracle tree," has gained significant attention in recent years due to its role in addressing global food security challenges and mitigating malnutrition. This article explores the diverse benefits of Moringa, highlighting its potential to combat hunger, alleviate malnutrition, and improve overall health worldwide.
The Global Food Security Crisis

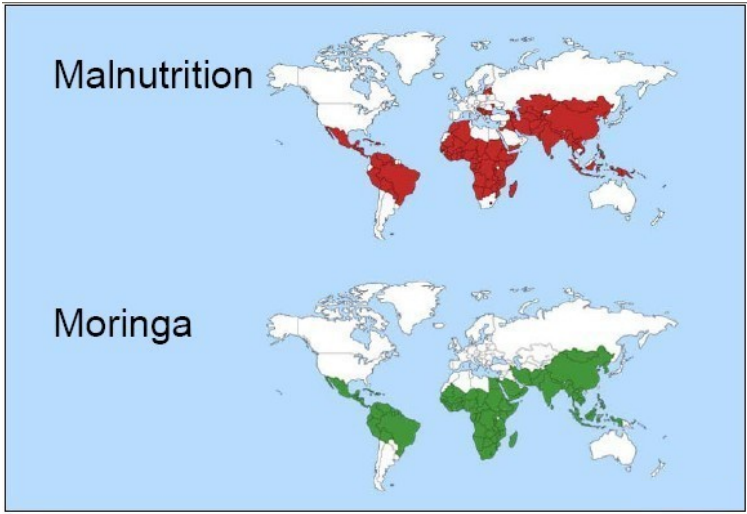
The global food security crisis remains one of the most daunting challenges of our time, with over 690 million people grappling with chronic hunger and countless others facing malnutrition. This crisis is particularly acute in developing nations, where access to nutritious food is often limited by economic, environmental, and social factors. The quest for sustainable solutions to address hunger and malnutrition is urgent, and in this context, Moringa Oleifera emerges as a beacon of hope.
Understanding the Crisis
- Root Causes: The food security crisis is driven by a complex web of factors including poverty, climate change, war, displacement, and unequal food distribution. These elements contribute to the scarcity of food and lack of access to nutritious options for vulnerable populations.
- Impact on Health: Chronic hunger and malnutrition lead to severe health problems, including stunted growth in children, weakened immunity, and increased susceptibility to diseases. The cycle of malnutrition and poor health perpetuates poverty and limits economic development.
Moringa: A Nutritional Powerhouse in the Fight against Hunger

Moringa Oleifera, often hailed as the "Miracle Tree," is increasingly recognized for its potential to combat malnutrition and bolster food security. Every part of the Moringa tree, from its leaves and bark to its flowers and seeds, is edible and rich in nutrients and bioactive compounds.
Nutrient-Dense Composition
- Vitamins and Minerals: Moringa leaves are an excellent source of vitamins A, C, and E, calcium, potassium, and iron, essential for immune function, bone health, and oxygen transport.
- Proteins and Antioxidants: The leaves contain all nine essential amino acids, making it a rare plant-based source of complete protein. Antioxidants such as quercetin and chlorogenic acid in Moringa help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Addressing Malnutrition
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating Moringa into the diet can significantly improve nutritional intake, especially in regions where access to a variety of foods is limited. Its high nutrient content can help address deficiencies and support overall health.
- Sustainable Cultivation: Moringa is drought-resistant and can be grown in a range of climates, making it an ideal crop for enhancing food security in arid and semi-arid regions. Its rapid growth and ability to thrive in poor soil conditions allow for multiple harvests per year, providing a continuous source of nutrition.
Leveraging Moringa for Global Food Security
Scalable Solutions
- Community Farming Projects: Initiatives that encourage the cultivation of Moringa at the community level can empower individuals and families to produce their own nutrient-rich food, reducing dependence on external food aid.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the nutritional benefits of Moringa and providing training on how to grow, harvest, and incorporate it into meals can enhance its adoption and impact on diet quality.
Policy Support and Research
- Government and NGO Involvement: Support from governments and non-governmental organizations can help scale Moringa cultivation projects, integrate Moringa into public health nutrition programs, and fund research on its benefits and uses.
- Innovative Food Products: Research into developing Moringa-based food products, such as fortified flours, protein powders, and snack bars, can increase its accessibility and convenience, making it easier for people to incorporate into their diets.
Moringa's Contribution to Global Food Security
Moringa trees flourish in various climates and require minimal water, making them suitable for cultivation in regions where agriculture faces challenges. This resilient plant provides a reliable source of nutrition, as its leaves can be consumed fresh or dried, and its seeds can be used to extract nutrient-rich oil. Incorporating Moringa into diets can enhance food diversity and contribute to long-term sustainable options for communities experiencing food scarcity.

Increased Crop Yield
In addition to being a valuable food source, Moringa also acts as a natural growth enhancer for other crops. When used as a fertilizer, Moringa leaf powder enriches the soil with essential nutrients, stimulating plant growth and increasing crop yield. This innovative agricultural practice can address food shortages while reducing reliance on chemical-based fertilizers.
Livestock Feed
Moringa leaves serve as an excellent source of fodder for livestock. By integrating Moringa into animal diets, farmers can improve the quality of feed and enhance the health and productivity of their herds. This holistic approach provides sustainable benefits by ensuring healthier livestock and increased food production.
Moringa as a Tool for Malnutrition Mitigation
Moringa's rich nutritional profile positions it as a potential solution to mitigate malnutrition. Among its various applications, Moringa-based products can be easily incorporated into therapeutic feeding programs, helping vulnerable populations recover from severe malnourishment.
Moringa in the Fight Against Childhood Malnutrition
Childhood malnutrition remains a pressing issue that requires immediate attention. Moringa-based formulations have been successfully used to treat malnourished children, delivering essential nutrients and promoting healthy growth. This natural remedy could revolutionize current malnutrition treatment strategies, offering an accessible and cost-effective solution.
Addressing Micronutrient Deficiencies
Micronutrient deficiencies, often referred to as hidden hunger, contribute significantly to malnutrition worldwide. Moringa's leaves boast high concentrations of essential vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, and vitamin A, combating these deficiencies when incorporated into diets. By bridging the nutritional gap, Moringa has the potential to improve overall health outcomes and prevent severe health issues resulting from malnutrition.
Conclusion
Moringa's role in global food security and malnutrition mitigation is undeniably significant. Its abundance of essential nutrients, adaptability in various environments, and potential to enhance crop yield make it a valuable asset for addressing hunger and malnutrition. By harnessing the power of Moringa, we can strive towards a more sustainable and nourished future for all, leaving no one behind.